1) Ethanol can be oxidised by complete combustion. With excess oxygen the complete combustion of ethanol (C₂H₅OH) in air produces carbon dioxide and water:
C₂H₅OH (l) + 3O₂ (g) → 2CO₂ (g) + 3H₂O (l)
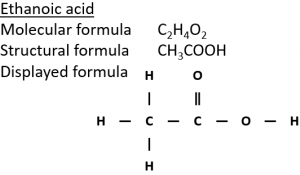
2) Ethanol can be oxidised in air in the presence of microorganisms (‘microbial oxidation’) to form ethanoic acid (CH₃COOH).
3) Ethanol can be oxidised by heating with the oxidising agent potassium dichromate(VI) (K₂Cr₂O₇) in dilute sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
In the equation below, [O] means oxygen from an oxidising agent.
CH₃CH₂OH + 2[O] → CH₃COOH + H₂O
This mixture starts orange but when the reaction happens turns green which indicates the presence of Cr³⁺ ions which are formed when the potassium dichromate(VI) is reduced.