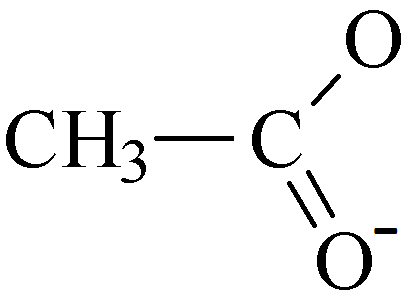Dilute carboxylic acids react with metals in the same way as other dilute acids (e.g. hydrochloric acid) only more slowly.
For example, dilute ethanoic acid reacts with magnesium with a lot of fizzing to produce a salt and hydrogen, leaving a colourless solution of magnesium ethanoate:
magnesium + ethanoic acid → magnesium ethanoate + hydrogen
Mg (s) + 2CH₃COOH (aq) → (CH₃COO)₂Mg (aq) + H₂ (g)
Dilute carboxylic acids react with metal carbonates as they do with other acids, to give a salt, carbon dioxide and water.
For example, dilute ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate with a lot of fizzing to produce a salt, carbon dioxide and water, leaving a colourless solution of sodium ethanoate:
sodium carbonate + ethanoic acid → sodium ethanoate + carbon dioxide + water
Na₂CO₃ (s) + 2CH₃COOH (aq) → 2CH₃COONa (aq) + CO₂ (g) + H₂O (l)
As can be seen in the examples above the charge on the ethanoate ion is -1.