1.30 know and use the relationship between the moment of a force and its perpendicular distance from the pivot
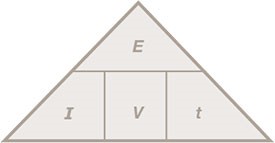
moment = force x perpendicular distance from the pivot
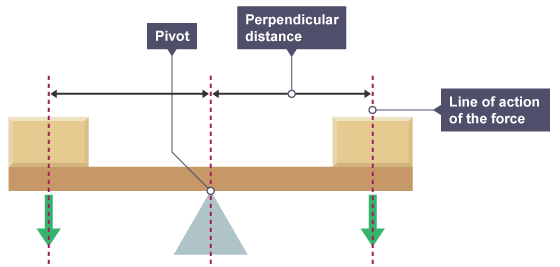
moment = force x perpendicular distance from the pivot

The principle of moments states that when the clockwise moments are equal to the anticlockwise moments a body will be in equilibrium.
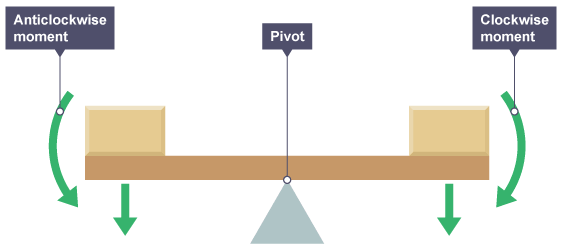
when moments are taken from the right hand side as the block is a greater distance the force from the left hand pivot must be bigger to counteract it. The opposite is true for the left hand side.
unit for:
current : Ampere (A)
charge : coulomb (C)
resistance : ohm (Ω)
time : second (s)
potential difference : volt (V)
power : watt (W)
Fuses Stop the flow of current by melting if the current is too high. So protecting sensitive components and people because if the components function at too higher temperature it can cause a fire.
Circuit breakers again break the circuit if current is too high.
Insulation and double insulation prevent people from touching exposed wires and getting shocks.
Earthing provides a low resistance path to the earth so if some one does come into contact with a current instead of flowing through them to the earth giving them a shock it flows through the earthing wire.
|
Resistance causes transfer of electrical energy to heat energy. Some components are designed to have a high resistance to make sure this happens, for example electrical heaters that have lots of resistors to ensure a high resistance so a lot of heat is produced. |
power (w) = current (A) x voltage (V)
when looking at a circuit a component will be given a power and a voltage appropriate to run at then the current can be calculated so the rating of the fuse can be selected for slightly higher than that.
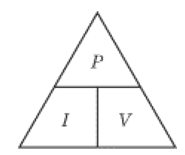
Energy (J) = potential difference (V) x current (A) x Time (s)
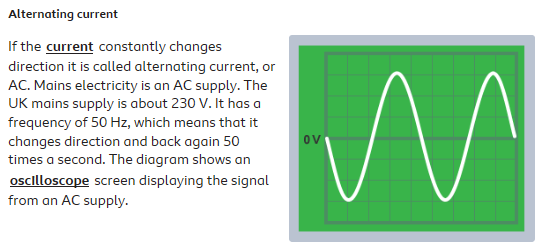
AC is constantly changing magnitude and direction. AC is how mains electricity is produced from turbines.
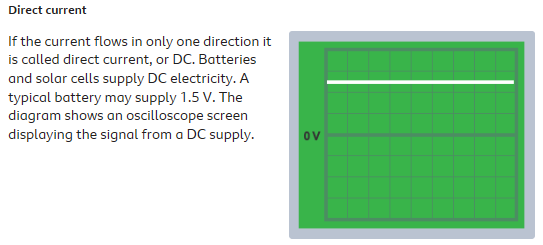
DC is constant. And is produced from a battery and used in some sensitive components like in computing.
Advantages of parallel circuits:
Advantages of series circuits:
Notes on current:
in the bellow diagram the red box could represent a wire, a bulb, a resistor or a diode.
By changing the resistance of the variable resistor the graphs are reproduced.
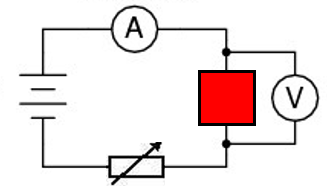
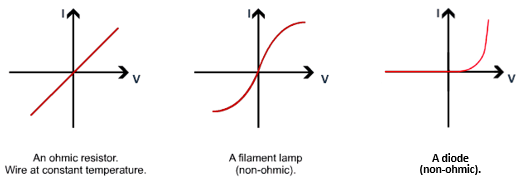
Since V = IR, as you increase the resistance in a circuit, the current will decrease.
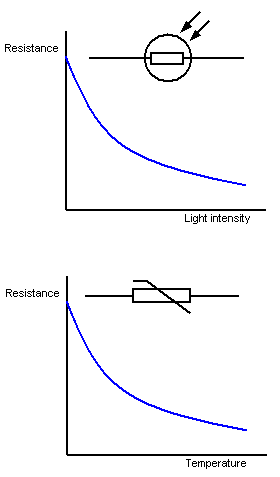
LDR
As illumination increases, resistance decreases
Thermistor
As temperature increases, resistance decreases.
A lamp can be added to a circuit to check for a current. If current is flowing, the lamp will light up.
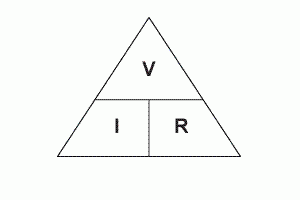
Potential difference (V) = Current (A) x Resistance (Ω)
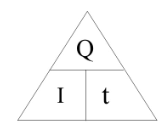
current is rate of flow of charge so I=Q/t
Charge (C) = Current (A) x Time (s)
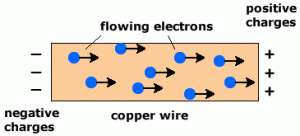
Electrons are negatively charged and free to flow in a metal so carry charge
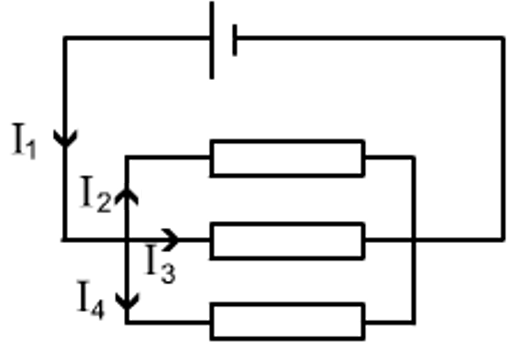
At a junction current ‘splits’ to take both paths.
It comes back together when the paths meet again.
I1 = I2 + I3 +I4
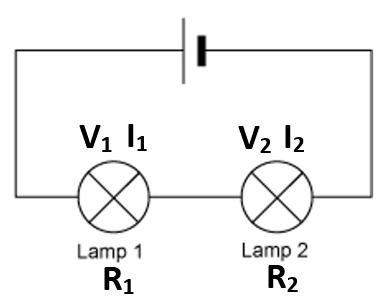
VT = V1 + V2
IT = I1 = I2
RT = R1 + R2
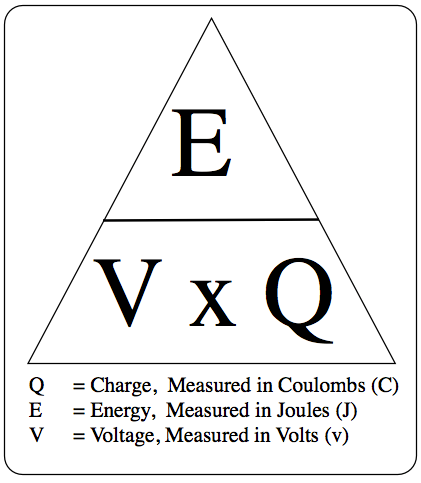
Energy Transferred (J) = charge (C) x Voltage (V)
Conducting Materials:
Will conduct electricity
Insulating Materials:
Will not conduct electricity
|
Paper is charged negatively in certain regions. Then positively charged paint droplets are sprayed onto the paper and attracted to the negative regions of the paper giving the desired image. |
the units for:
angle = degree (°)
frequency = hertz (Hz)
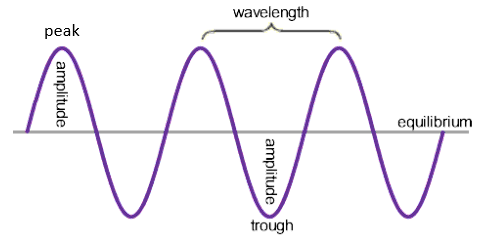
wavelength = metre (m)
velocity = metre/second (m/s)
time = second (s)
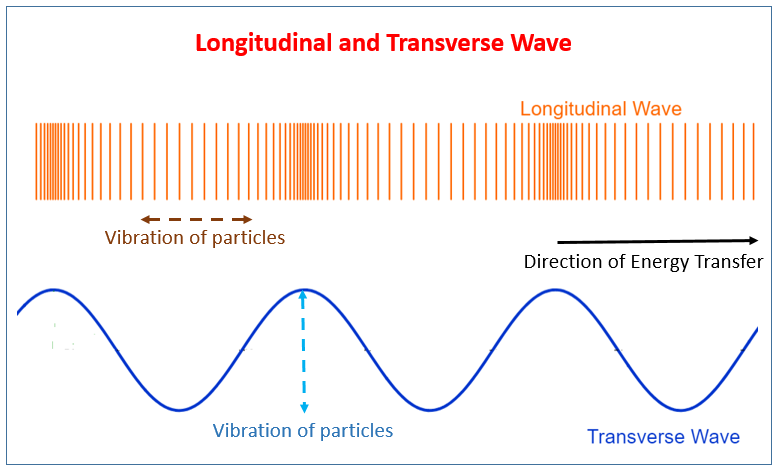
Transverse Waves:
Longitudinal Waves:
Key Definitions:
Waves can transfer energy and information with out transferring matter, for example sun light, it transfers energy as it makes the earth warm without bringing any matter.
wave speed (m/s) = frequency (Hz) x Wavelength (m)
Frequency (Hz) = 1/ Time Period (s)
You will need to use any of the in 3.05 and 3.06 to solve problems to do with sound waves and electromagnetic (light) waves
Doppler Effect:
Electromagnetic Spectrum:
Radio Waves
Microwaves
Infrared (IR)
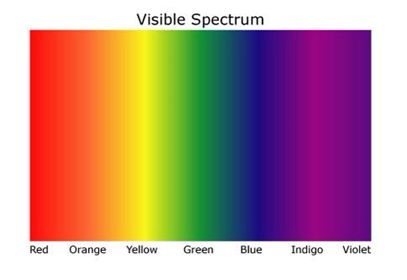
Visible Light
Ultraviolet (UV)
X – Rays
Gamma Rays
these are written in order of increasing frequency, lowest at the top
and decreasing wavelength, lowest at the bottom.
the colours displayed are in order of lowest frequency to the left highest frequency to the right.
|
uses of electromagnetic radiations, including: |
the detrimental effects of excessive exposure of the human body to electromagnetic waves:
• microwaves: internal heating of body tissue
• infrared: skin burns
• ultraviolet: damage to surface cells and blindness
• gamma rays: cancer, mutation
to reduce the risks:
light is a transverse wave that can be reflected and refracted
|
1. Set up your apparatus as shown in the diagram using a rectangular block. 2. Shine the light ray through the glass block 3. Use crosses to mark the path of the ray. 4. Join up crosses with a ruler 5. Draw on a normal where the ray enters the glass block 6. Measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction and add these to your results table 7. Comment on how the speed of the light has changed as the light moves between the mediums. 8. Repeat this for different angles of incidence and different glass prisms. |