3:17 know that some reactions are reversible and this is indicated by the symbol ⇌ in equations
Some reactions are reversible. This is indicated by the symbol ⇌
For example:
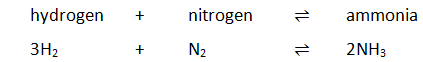
Some reactions are reversible. This is indicated by the symbol ⇌
For example:
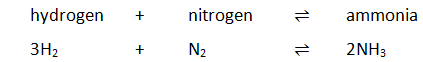
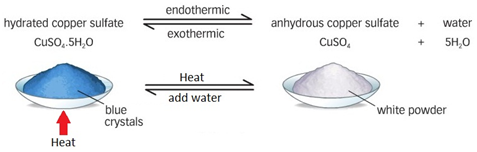
Dehydration of copper(II) sulfate
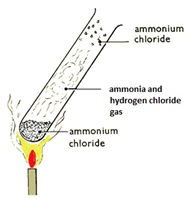 Heating ammonium chloride
Heating ammonium chloride
On heating, white solid ammonium chloride decomposes forming ammonia and hydrogen chloride gas. On cooling, ammonia and hydrogen chloride react to form a white solid of ammonium chloride:
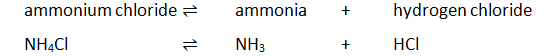
A dynamic equilibrium can only be achieved in a sealed container so substances cannot escape.
Features of a reaction mixture that is in dynamic equilibrium:
A catalyst is a substance which increases the rate of reaction without being chemically changed at the end of the reaction.
A reversible reaction is one where the forward reaction and the backward reaction happen simultaneously. For example:
3H₂ + N₂ ⇋ 2NH₃
In such a reaction a catalyst speeds up both the forward and the backward reactions. Hence, although the system will reach dynamic equilibrium more quickly, the addition of a catalyst will not affect the position of equilibrium.
In a reversible reaction the position of the equilibrium (the relative amounts of reactants and products) is dependent on the temperature and pressure of the reactants.
If the conditions of an equilibrium reaction are changed, the reaction moves to counteract that change.
Therefore by altering the temperature or pressure the position of the equilibrium will change to give more or less products.
Adding a catalyst does not affect the position of the equilibrium.
If a change in conditions moves equilibrium to the right, the yield of the substances on the right is increased.
Changing the temperature:
All reactions are exothermic in one direction and endothermic in the other way.
For this reaction the enthalpy change, ΔH is negative therefore the forward reaction is exothermic:
CO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇌ CH3OH(g) ΔH = –91 kJ/mol
If temperature is decreased the position of the equilibrium will shift to the right because it is an exothermic reaction.
For this reaction the enthalpy change, ΔH is positive therefore the forward reaction is endothermic:
CH4(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO(g) + 3H2(g) ΔH = +210 kJ mol–1
If temperature is increased the position of the equilibrium will shift to the right because it is an endothermic reaction.
Key point: an increase (or decrease) in temperature shifts the position of equilibrium in the direction of the endothermic (or exothermic) reaction
Changing the pressure:
Reactions may have more molecules of gas on one side than on the other.
For this reaction there are 2 molecules on the left and 4 molecules on the right:
CH4(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO(g) + 3H2(g) ΔH = +210 kJ mol–1
If the pressure is increased the position of the equilibrium will shift to the left because there are fewer molecules on the left-hand side.
For this reaction there are 3 molecules on the left and 1 molecule on the right
CO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇌ CH3OH(g) ΔH = –91 kJ/mol
If the pressure is decreased the position of the equilibrium will shift to the left because there are more molecules on the left-hand side.
Key point: an increase (or decrease) in pressure shifts the position of equilibrium in the direction that produces fewer (or more) moles of gas