4:38 (Triple only) know that esters contain the functional group -COO-
Esters contain the functional group -COO-
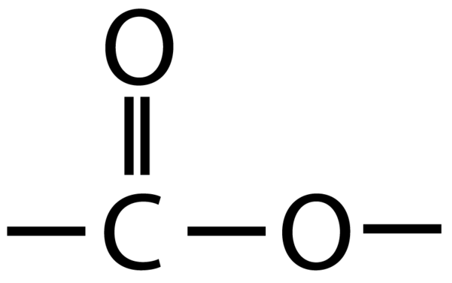
An example of an ester is ethyl ethanoate:
Esters contain the functional group -COO-
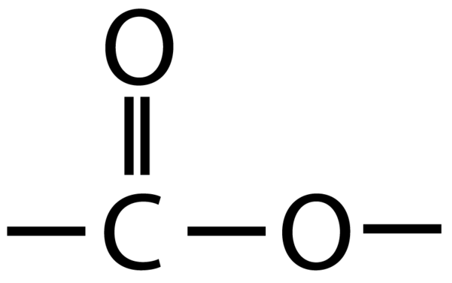
An example of an ester is ethyl ethanoate:

Ethyl ethanoate is the ester produced when ethanol and ethanoic acid react in the presence of an acid catalyst.
ethanoic acid + ethanol ⇋ ethyl ethanoate + water
CH₃COOH (l) + CH₃CH₂OH (l) ⇋ CH₃COOCH₂CH₃ (l) + H₂O (l)
The ethyl ethanoate produced is an ester.
The reaction is called esterification.
The reaction can also be described as a condensation reaction because water is made when two molecules join together.
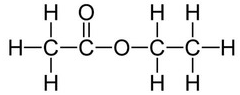
Ethyl ethanoate is an ester.
Structural formula: CH₃COOCH₂CH₃
Displayed formula:
To work out the structure of the ester formed when an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid, it is easiest to first draw the structures of alcohol and acid and then remove the H₂O to see what is left when the molecules join.
For example, propan-1-ol and ethanoic acid react together to form propyl ethanoate and water.
propan-1-ol + ethanoic acid → propyl ethanoate + water
CH₃CH₂CH₂OH (l) + CH₃COOH (l) → CH₃COOCH₂CH₂CH₃ (l) + H₂O (l)
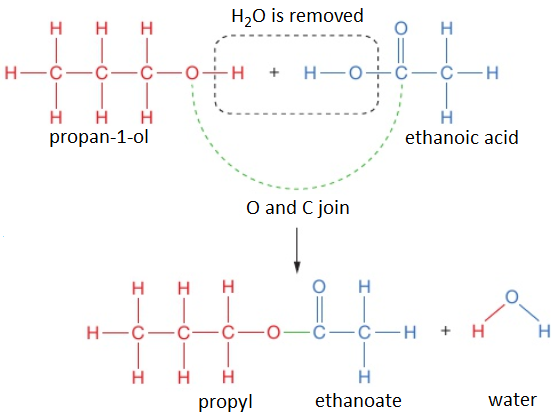
The displayed formula for esters is typically written to show the part which came from the carboxylic acid on the left:
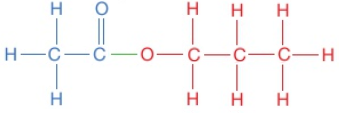
This is still called propyl ethanoate: the alcohol bit of the name (propyl) comes first and then the carboxylic acid bit (ethanoate), even though the displayed formula is typically written the other way around. Notice that the structural formulae for esters is also typically written with the carboxylic acid bit first, so propyl ethanoate is CH₃COOCH₂CH₂CH₃.
Esters are volatile compounds with distinctive smells. A volatile liquid is one that turns into to a vapour easily.
Esters are used as food flavourings and in perfumes.
Esters are often described as having a sweet, fruity smell. They typically smell of bananas, raspberries, pears or other fruit because esters occur in all these natural products.
Heating a mixture of ethanoic acid and ethanol produces a liquid called ethyl ethanoate. A few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid must be added for the reaction to work. The sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst.
ethanoic acid + ethanol ⇋ ethyl ethanoate + water
CH₃COOH (l) + CH₃CH₂OH (l) ⇋ CH₃COOCH₂CH₃ (l) + H₂O (l)
The ethyl ethanoate produced is an ester.
The reaction is called esterification.
The reaction can also be described as a condensation reaction because water is made when two molecules join together.
Notice that the reaction is reversible. Pure reactants are used to maximise the yield of ethyl ethanoate. Pure ethanoic acid is called glacial ethanoic acid.