Example: When calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is heated calcium oxide is produced. You can use reacting mass calculations to calculate the mass of calcium oxide produced when heating 25 g of calcium carbonate.
CaCO3 –> CaO + CO2
Step 1: Calculate the amount, in moles, of 25 g of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
Step 2: Deduce the amount, in moles, of CaO produced from 0.25 mol of CaCO3.
This step involves using the ratio of CaCO3 to CaO from the chemical equation.
CaCO3 –> CaO + CO2
From the equation you can see that the ratio of CaCO3 to CaO is 1:1.
Therefore if you have 0.25 mol of CaCO3 this will produced 0.25 mol of CaO.
Step 3: Calculate the mass of 0.25 mol of CaO.
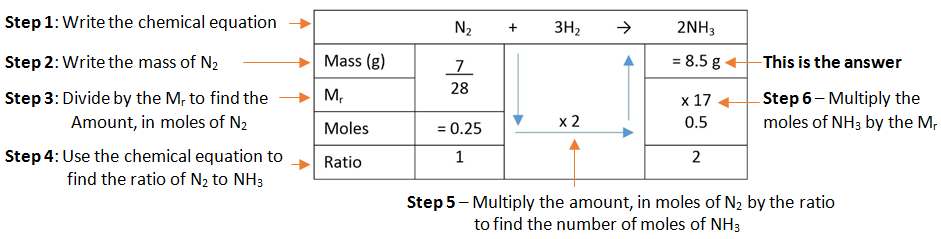
A simple format for laying out this method can be used.
Example: What mass of ammonia (NH3) is formed when 7 g of nitrogen (N2) is combined with hydrogen (H2).