1:35 (Triple only) understand how to carry out calculations involving gas volumes and the molar volume of a gas (24dm³ and 24,000cm³ at room temperature and pressure (rtp))
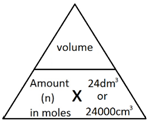
The molar volume of a gas is the volume that one mole of any gas will occupy.
1 mole of gas, at room temperature and pressure (rtp), will always occupy 24 dm3 or 24,000 cm3.
Note: 1 dm3 = 1000 cm3
The following formulae allows for the interconversion between a volume in dm3 or cm3 and a number of moles for a given gas:
or
Example 1:
Calculate the amount, in moles, of 12 dm3 of carbon dioxide (CO2).
Example 2:
Calculate the volume at rtp in cubic centimetres (cm3), of 3 mol of oxygen, (O2).