1:07 (Triple only) practical: investigate the solubility of a solid in water at a specific temperature
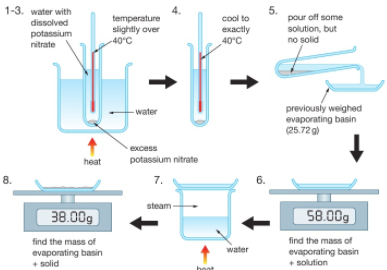
At a chosen temperature (e.g. 40⁰C) a saturated solution is created of potassium nitrate (KNO₃) for example.
Some of this solution (not any residual solid) is poured off and weighed. The water is then evaporated from this solution to leave a residue of potassium nitrate which is then weighed.
The difference between the two measured masses is the mass of evaporated water.
The solubility, in grams per 100g of water, is equal to 100 times the mass of potassium nitrate residue divided by the mass of evaporated water.