4:31 (Triple only) know that ethanol can be oxidised by: burning in air or oxygen (complete combustion), reaction with oxygen in the air to form ethanoic acid (microbial oxidation), heating with potassium dichromate(VI) in dilute sulfuric acid to form ethanoic acid
1) Ethanol can be oxidised by complete combustion. With excess oxygen the complete combustion of ethanol (C₂H₅OH) in air produces carbon dioxide and water:
C₂H₅OH (l) + 3O₂ (g) → 2CO₂ (g) + 3H₂O (l)
2) Ethanol can be oxidised in air in the presence of microorganisms (‘microbial oxidation’) to form ethanoic acid (CH₃COOH).
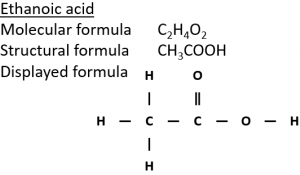
3) Ethanol can be oxidised by heating with the oxidising agent potassium dichromate(VI) (K₂Cr₂O₇) in dilute sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
In the equation below, [O] means oxygen from an oxidising agent.
CH₃CH₂OH + 2[O] → CH₃COOH + H₂O
This mixture starts orange but when the reaction happens turns green which indicates the presence of Cr³⁺ ions which are formed when the potassium dichromate(VI) is reduced.