4.14 know and use the relationship: kinetic energy = 1/2×m×v^2
Kinetic energy (J) = 0.5 x mass (kg) x velocity (m/s) 2
Kinetic energy (J) = 0.5 x mass (kg) x velocity (m/s) 2
Because energy is conserved the decrease in GPE = increase in KE, for a falling object if no energy is lost to the surroundings
power is the rate of transfer of energy, or the rate of work done. so p = E/t
The units for:
temperature: degree Celsius (°C) or Kelvin (K)
Energy: Joule (J)
mass: Kilogram (kg)
density: kilogram/metre cubed (kg/m3)
distance: metre (m)
area: metre squared (m2)
volume: metre cubed (m3)
velocity: metre per second (m/s)
acceleration: metre per second squared (m/s2)
force: newton (N)
pressure: pascal (Pa)
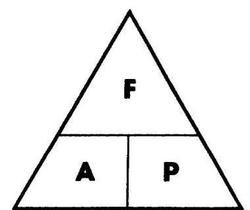
pressure (Pa) = force (N)/ area (m2)
Pressure in liquids:
Pressure in liquids acts equally in all directions as long as the liquid is not moving.
Gas laws:
Absolute zero:
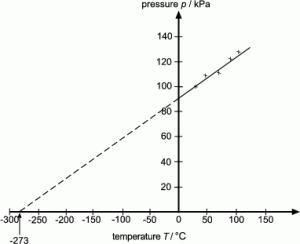
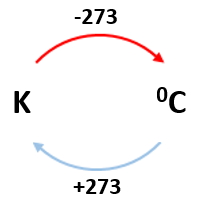
0 K = -273 0C
E.g. 100K = -1730C
2000C = 473K
As you increase the temperature of a gas, the kinetic energy of the gas particles increases and thus their average speed also increases.
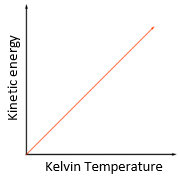
The Kelvin temperature of a gas is proportional to the average kinetic energy of its molecules.
The unit for:
Current : amps (A)
Potential Difference : volt (V)
power : watt (W)
Around every magnet there is a region of space where we can detect magnetism (where magnetic materials will be affected).
This is called the magnetic field and in a diagram we represent this with magnetic field lines.
The magnetic field lines should always point from north to south.
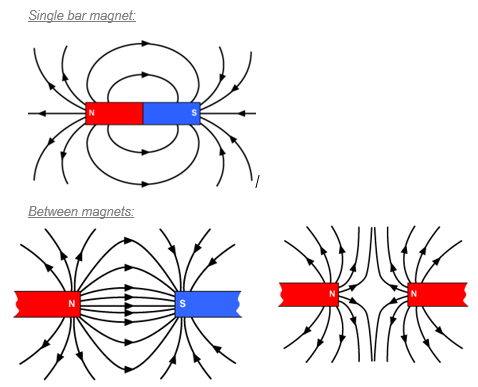
|
A uniform magnetic field is comprised of straight, parallel lines which are evenly spaced. Between two opposite charges on flat magnets, a uniform magnetic field is formed. |
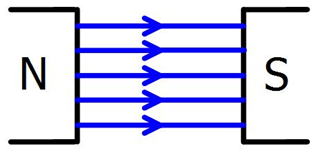
|
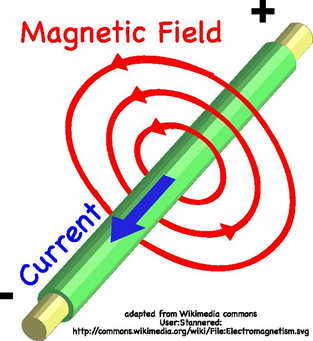
A current travelling along a wire produces a circular magnetic field around the wire. The magnetic field direction can be determined using the right hand grip rule. |
Motor
Loudspeaker
|
Fleming’s left hand rule. Thumb: force First finger: Magnetic Field Second finger: Current |
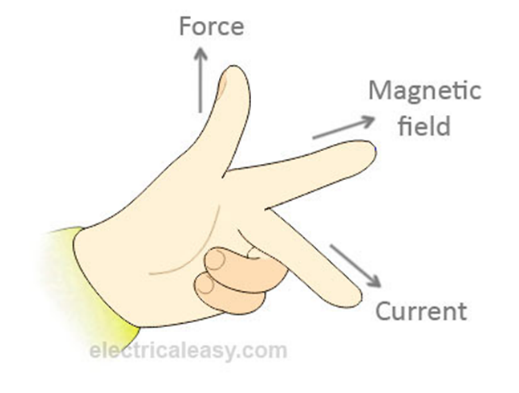
|
If you increase the magnitude of the current through a wire or the size of the magnet being used, you increase the force on the wire. If you change the direction of the current or reverse the poles of the magnet, you change the direction of the force on the wire |
the units for:
frequency of decay : becquerel (Bq), 1 (Bq) for 1 decay / sec
distance : centimetres (cm), normally however is (m)
time : hour (h), minute (min) but normally (s)
Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons.
Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, electrons are in the shells
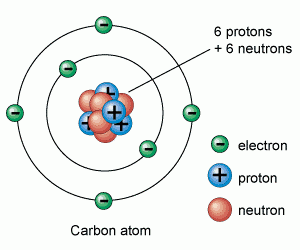
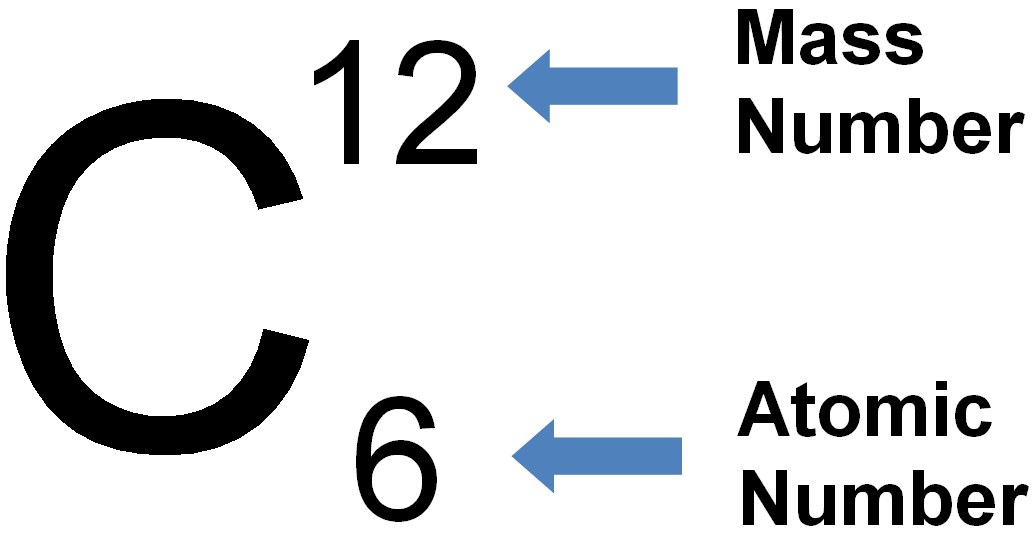
|
Atomic (proton) number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass (nucleon) number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. An isotope is an atom of the same element, i.e. it has the same number of protons/same atomic number, but has a different number of neutrons/different mass number. Two atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers are isotopes see 7.02 for example |
There are three types of ionising radiation:
Alpha (α), Beta (β) and Gamma (γ)
One radioactive source can release different types of radiation.
Ionisation is when an atom loses or gains an electron, causing it to become an ion (an atom which is positively or negatively charged).
|
Detect using a Geiger Müller Tube. Try the three different materials in order, paper then aluminium then lead. Count rate will significantly decrease if radiation is stopped. |
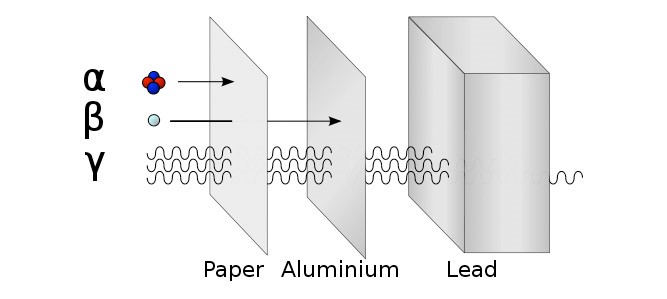
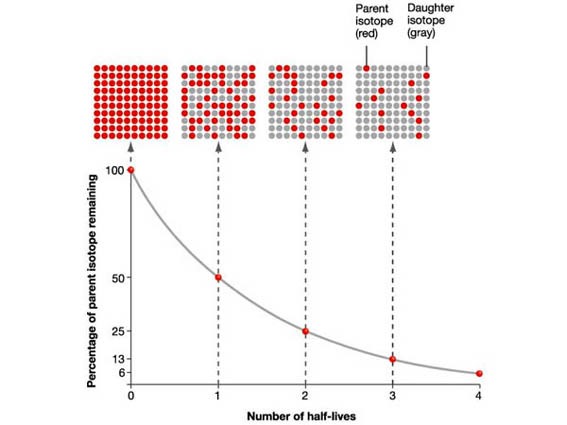
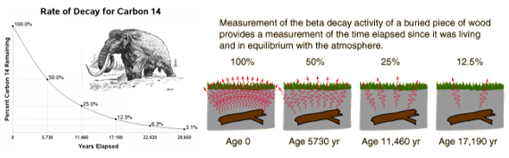
The Half-life is the time taken for the radioactivity of a specific isotope to fall to half its original value.
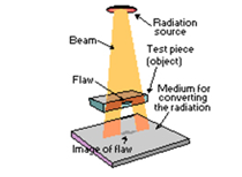
Gamma radiography:
|
Medical tracer: – Radioactive tracer put in body (swallowed/injected) – Detector put around body – Computer generates an image |

|
Gauging: – Coal absorbs a lot of radiation – If only a small amount of radiation is detected back after it is reflected by what you are trying to gauge, lots of coal is present. |

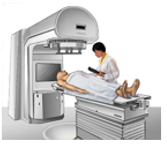
Radiotherapy
|
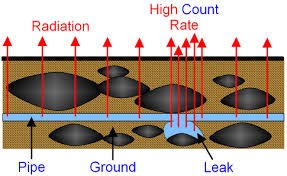
Pipe tracers: – A radioactive material which emits gamma radiation with a short half-life is put in the water – A detector is placed above the pipe – A spike in detected radioactivity suggests a leak in the pipe |
Sterilisation:

Carbon dating:
Occurs when material that contains radioactive atoms is deposited on materials, skin, clothing, or any place where it is not desired.
The process by which an object is exposed to radiation.
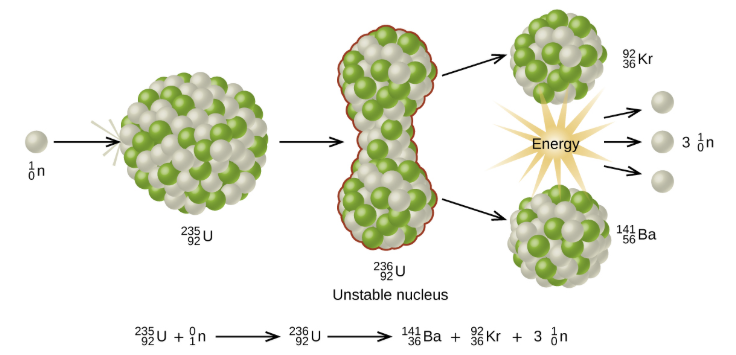
The process where heavy atoms are split into smaller, lighter atoms. This releases energy.
The process where lighter atoms are forced to join together to make heavier atoms. This releases energy.
Within the core of the Earth, radioactive isotopes of elements such as uranium, thorium and potassium provide a large proportion of the heat within the Earth through radioactive decay.
Shielding:
units for:
Mass: kilogram (kg)
distance: metre (m)
velocity: metre per second (m/s)
acceleration: metre per second squared (m/s2)
Force: newton (N)
time: second (s)
gravitational field strength: newton/kilogram (N/kg)