3.01 use the following units: degree (°), hertz (Hz), metre (m), metre/second (m/s) and second (s)
the units for:
angle = degree (°)
frequency = hertz (Hz)
wavelength = metre (m)
velocity = metre/second (m/s)
time = second (s)
the units for:
angle = degree (°)
frequency = hertz (Hz)
wavelength = metre (m)
velocity = metre/second (m/s)
time = second (s)
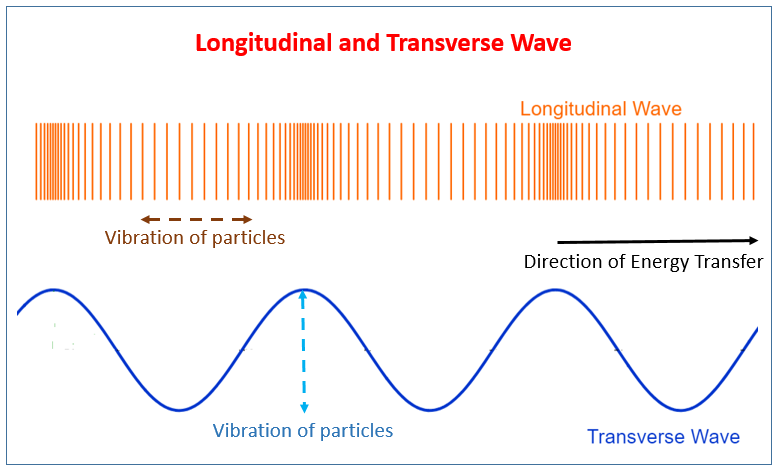
Transverse Waves:
Longitudinal Waves:
Key Definitions:
Waves can transfer energy and information with out transferring matter, for example sun light, it transfers energy as it makes the earth warm without bringing any matter.
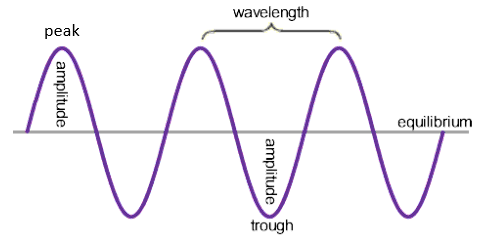
wave speed (m/s) = frequency (Hz) x Wavelength (m)
Frequency (Hz) = 1/ Time Period (s)
You will need to use any of the in 3.05 and 3.06 to solve problems to do with sound waves and electromagnetic (light) waves
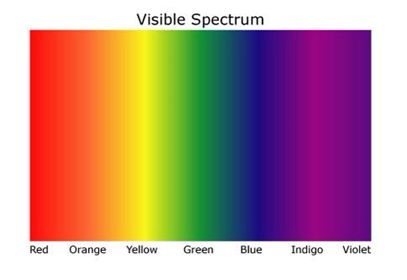
Electromagnetic Spectrum:
Radio Waves
Microwaves
Infrared (IR)
Visible Light
Ultraviolet (UV)
X – Rays
Gamma Rays
these are written in order of increasing frequency, lowest at the top
and decreasing wavelength, lowest at the bottom.
the colours displayed are in order of lowest frequency to the left highest frequency to the right.
|
uses of electromagnetic radiations, including: |
the detrimental effects of excessive exposure of the human body to electromagnetic waves:
• microwaves: internal heating of body tissue
• infrared: skin burns
• ultraviolet: damage to surface cells and blindness
• gamma rays: cancer, mutation
to reduce the risks:
|
1. Set up your apparatus as shown in the diagram using a rectangular block. 2. Shine the light ray through the glass block 3. Use crosses to mark the path of the ray. 4. Join up crosses with a ruler 5. Draw on a normal where the ray enters the glass block 6. Measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction and add these to your results table 7. Comment on how the speed of the light has changed as the light moves between the mediums. 8. Repeat this for different angles of incidence and different glass prisms. |
|
1. Set up your apparatus as shown in the diagram using a rectangular block. 2. Shine the light ray through the glass block 3. Use crosses to mark the path of the ray. 4. Join up crosses with a ruler 5. Draw on a normal where the ray enters the glass block 6. Measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction and add these to your results table 7. Calculate the refractive 8. Repeat steps 2 – 7 using 9. Find an average of your
|
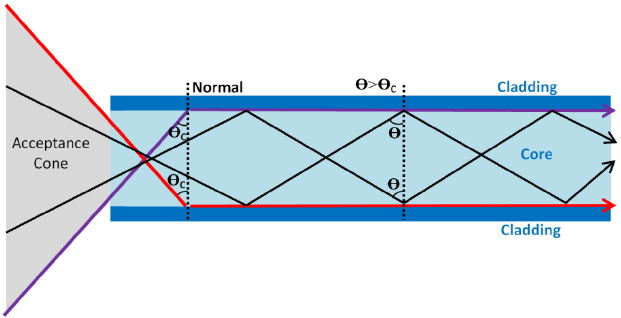
Total Internal Reflection:
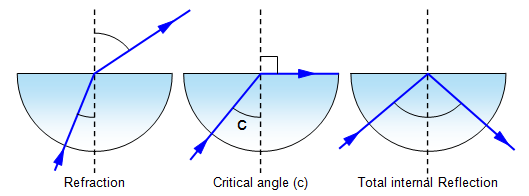
Critical Angle:
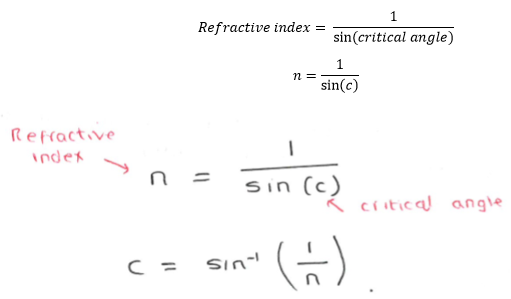
also remember:
critical angle = sin-1(1/n)
sound waves are longitudinal waves which can be reflected and refracted.