6.01 use the following units: ampere (A), volt (V) and watt (W)
The unit for:
Current : amps (A)
Potential Difference : volt (V)
power : watt (W)
The unit for:
Current : amps (A)
Potential Difference : volt (V)
power : watt (W)
Opposites attract: North attracts South and South attracts North
Like charges repel: Two Norths will repel each other
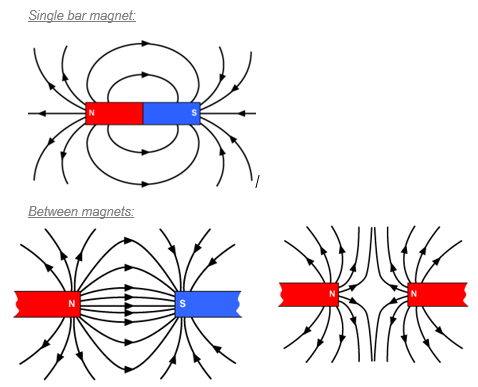
Around every magnet there is a region of space where we can detect magnetism (where magnetic materials will be affected).
This is called the magnetic field and in a diagram we represent this with magnetic field lines.
The magnetic field lines should always point from north to south.
|
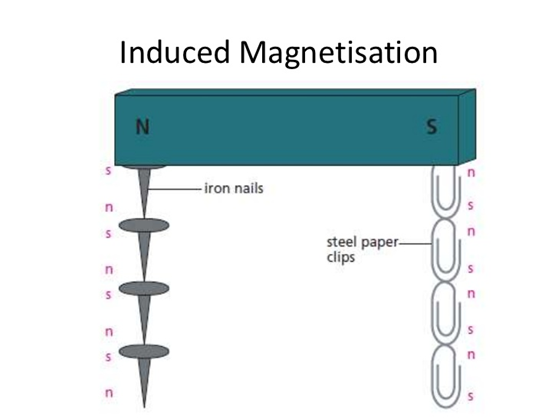
When magnetic materials are bought near or touch the pole of a strong or permanent magnet, they become magnets. This magnetic character is induced in the objects and it is removed when the permanent magnet is removed. This is a temporary magnet Magnetism is induced in the paperclips so each paperclip can attract another one |
|
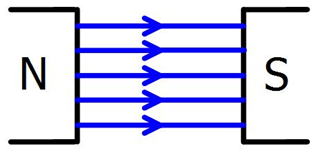
A uniform magnetic field is comprised of straight, parallel lines which are evenly spaced. Between two opposite charges on flat magnets, a uniform magnetic field is formed. |
|
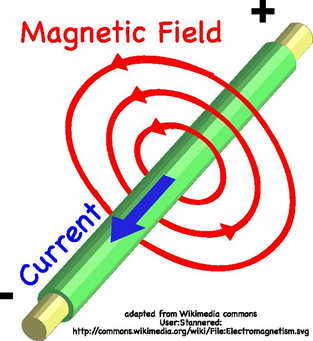
A current travelling along a wire produces a circular magnetic field around the wire. The magnetic field direction can be determined using the right hand grip rule. |
A soft iron core wrapped in wire. When current flows through the coil of wire it becomes magnetic.
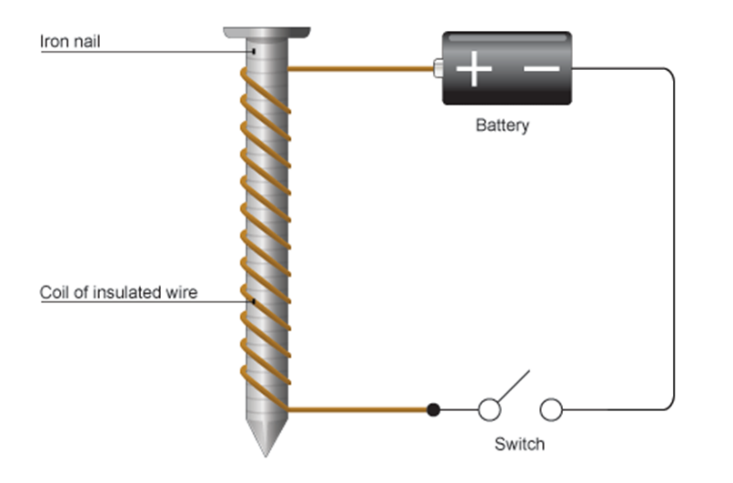
|
The movement of the charged particle is a current so it produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the permanent magnetic field to create a force. The force is perpendicular to the direction of motion and the permanent magnetic field. |
Motor
Loudspeaker
|
Fleming’s left hand rule. Thumb: force First finger: Magnetic Field Second finger: Current |
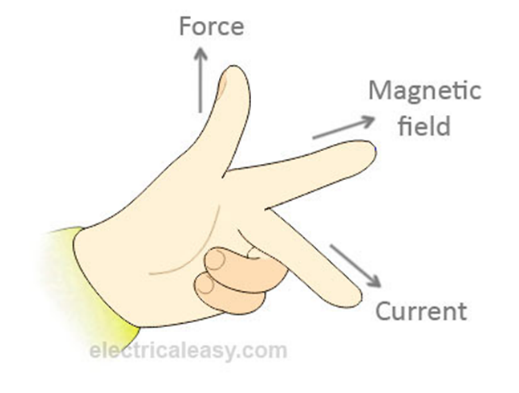
|
If you increase the magnitude of the current through a wire or the size of the magnet being used, you increase the force on the wire. If you change the direction of the current or reverse the poles of the magnet, you change the direction of the force on the wire |