Metal Reactivity & Halogens quiz
The elements in the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
Columns are called Groups. They indicate the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom.
Rows are called Periods. They indicate the number of shells (energy levels) in an atom.
Electrons are found in a series of shells (or energy levels) around the nucleus of an atom.
Each energy level can only hold a certain number of electrons. Low energy levels are always filled up first.
Rules for working out the arrangement (configuration) of electrons:
Example – chlorine (Cl)
1) Use the periodic table to look up the atomic number. Chlorine’s atomic number (number of protons) is 17.
2) Remember the number of protons = number of electrons. Therefore chlorine has 17 electrons.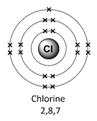
3) Arrange the electrons in levels (shells):
Therefore the electron arrangement for chlorine (17 electrons in total) will be written as 2,8,7
4) Check to make sure that the electrons add up to the right number
The electron arrangement can also be draw in a diagram.
Electron arrangement for the first 20 elements:
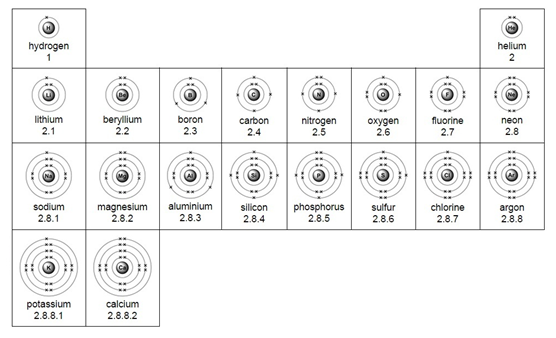
Metals
Non – Metals
Metals on the left of the Periodic Table.
Non-Metals on the top-right, plus Hydrogen.
Elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer shell.
This is why elements from the same group have similar properties.
Elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of electrons in their outer shells, which means they have similar chemical properties.
The noble gases are inert (unreactive) because they have a full outer shell of electrons.
Group 1 metals such as potassium, sodium and lithium, react with water to produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen. For example:
lithium + water → lithium hydroxide + hydrogen
2Li (s) + 2H₂O (l) → 2LiOH (aq) + H₂ (g)
The observations for the reaction of water with either potassium or sodium or lithium have the following similarities:
In each case a metal hydroxide solution is produced.
These similarities in the reactions provide evidence that the 3 metals are in the same group of the Periodic Table (i.e. have the same number of electrons in their outer shell).
Lithium is the first element in group 1 of the Periodic Table. The observations for the reaction of lithium and water are:
Sodium is the second alkali metal in the group. The reaction of sodium and water is more vigorous than lithium’s:
Potassium is the third alkali metal in the group. The reaction of potassium and water is more vigorous than sodium’s:
When the group 1 metals react with air they oxidise, showing a similar trend in reactivity as we go down the group of the Periodic Table.
Therefore, as we go down group 1 (increasing atomic number), the elements become more reactive: Li<Na<K<Rb<Cs<Fr
From the data in the table, it is possible to deduce the properties of francium from the trends in the other group 1 metals.
For example, we can predict that francium will have a melting point around 20⁰C and a density of just over 2g/cm³.
We can also predict that francium will react violently with water, producing francium hydroxide and hydrogen.
| Alkali metal | Melting point (⁰C) | Density (g/cm³) | Reaction with water | Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lithium (Li) | 181 | 0.53 | fizzing | lithium hydroxide + hydrogen |
| sodium (Na) | 98 | 0.97 | rapid fizzing | sodium hydroxide + hydrogen |
| potassium (K) | 63 | 0.86 | vigorous fizzing and lilac flame | potassium hydroxide + hydrogen |
| rubidium (Rb) | 39 | 1.53 | ? | rubidium hydroxide + hydrogen |
| caesium(Cs) | 29 | 1.88 | ? | caesium hydroxide + hydrogen |
| francium (Fr) | ? | ? | ? | ? |
The awesome Professor Sir Martyn Poliakoff shows us the reaction of some alkali metals and water.
As you go down the group the outer electron lost from the group 1 metal is further from the nucleus therefore the electron is less attracted by the nucleus and therefore more easily lost.
| Element | Colour | State at room temp |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorine (Cl2) | Green | Gas |
| Bromine (Br2) | Red-brown | Liquid |
| Iodine (l2) | Grey | Solid |
Chlorine is a toxic gas, so should be handled in a fume cupboard.
If you look at the trends in the physical properties of the halogens, Cl2, Br2, I2 you can make predictions about the properties of the other halogens.
| Element | Colour | State at room temp |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorine (F2) | Yellow | Gas |
| Astatine (At2) | Black | Solid |
Here is a great video on Fluorine, which is the most reactive halogen (group 7):
Group 7 elements are called the Halogens. As you go up group 7 (decreasing atomic number), the elements become more reactive. For example, fluorine is the most reactive and astatine is the least reactive.
A more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive halogen, e.g. chlorine will displace bromine:

By reacting a halogen solution with a potassium halide solution and making observations, the order of their reactivity can be deduced:
| Potassium chloride, KCl(aq) | Potassium bromide, KBr(aq) | Potassium iodide, KI(aq) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorine, Cl2(aq) | No change | Colourless to orange | Colourless to brown |
| Bromine, Br2(aq) | No change | No change | Colourless to brown |
| Iodine, I2(aq) | No change | No change | No change |
From the above results, chlorine displaces both bromine and iodine, and bromine displaces iodine. Therefore the order of reactivity is: chlorine is more reactive than bromine, which in turn is more reactive than iodine.
The reactions of various halogens with iron wool is a great way to see how reactive one halogen is compared to another:
Special thanks to Charlie R for suggesting I add a video on halogen displacement.
The higher up we go in group 7 (halogens) of the periodic table, the more reactive the element. The explanation concerns how readily these elements form ions, by attracting a passing electron to fill the outer shell.
In fluorine the outer electron shell is very close to the positively charged nucleus, so the attraction between this nucleus and the negatively charged electrons is very strong. This means fluorine is very reactive indeed.
However, for iodine the outer electron shell is much further from the nucleus so the attraction is weaker. This means iodine is less reactive.
 Some metals are more reactive than others.
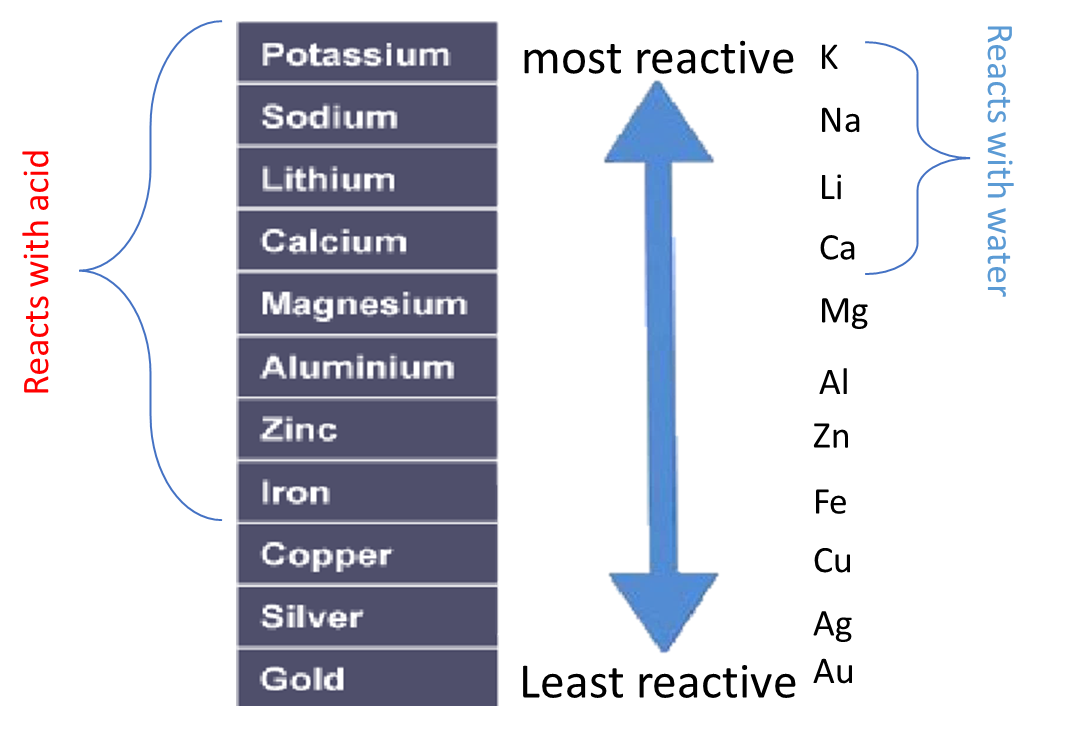
Some metals are more reactive than others.
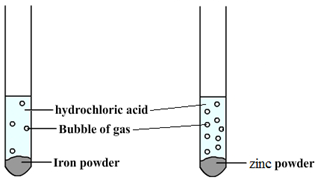
The order of reactivity can be determined by adding acid to different metals and observing the rate of reaction.
For example, when hydrochloric acid is added to iron (Fe) then bubbles of hydrogen are produced slowly. However, if the same acid is added to zinc (Zn) then bubbles will be produced more quickly. This tells us that zinc is more reactive than iron.
Instead of using acid, water can be used to test the relative reactivity of metals. However, many metals are too low in the reactivity series to react with water
A metal will displace another metal from its oxide that is lower in the reactivity series. For example, a reaction with magnesium and copper (II) oxide will result in the magnesium displacing the copper from its oxide:
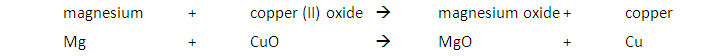
A metal will also displace another metal from its salt that is lower in the reactivity series. For example, the reaction between zinc and copper (II) sulfate solution will result in zinc displacing the copper from its salt:
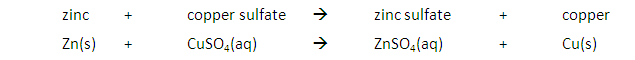
The blue colour of the copper (II) sulfate solution fades as colourless zinc sulfate solution is formed.
The thermite reaction is used to repair railways: the reaction between aluminium and iron oxide is highly exothermic and produces molten iron.
It should be properly controlled if demonstrated in the lab: watch this video and see how many mistakes in basic lab safety made by this teacher.
A more reactive metal will displace a less reactive metal.
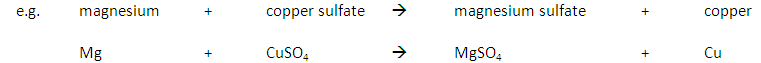
In addition a more reactive metal will react more vigorously than a less reactive metal.
For example, potassium takes a shorter time to react than sodium:
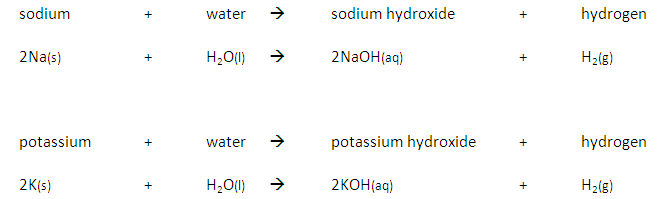
Iron rusts when oxygen and water are present.
Reaction:
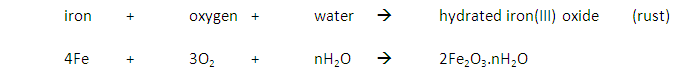
Barrier Methods: Rusting may be prevented by stopping the water and oxygen getting to the iron with a barrier of grease, oil, paint or plastic.
Galvanising: (coating in zinc) also prevents water and oxygen getting to the iron, but with galvanising even if the barrier is broken the more reactive zinc corrodes before the less reactive iron. During the process, the zinc loses electrons to form zinc ions.
Barrier Methods: Rusting may be prevented by stopping the water and oxygen getting to the iron with a barrier of grease, oil, paint or plastic.
Galvanising: (coating in zinc) also prevents water and oxygen getting to the iron, but with galvanising even if the barrier is broken the more reactive zinc corrodes before the less reactive iron. During the process, the zinc loses electrons to form zinc ions.
Sacrificial Protection: Zinc blocks are attached to iron boat hulls and underground pipelines to act as sacrificial anodes. Zinc is more reactive than iron, so oxygen in the air reacts with the zinc to form a layer of zinc oxide instead of the iron.
This video shows the galvanising of pieces of steel to protect them from rusting:
Oxidation
Reduction
Redox: A reaction involving oxidation and reduction.
A good way to remember the definitions of oxidation and reduction in terms of electrons is:
Oxidising agent: A substance that gives oxygen or removes electrons (it is itself reduced).
Reducing agent: A substance that takes oxygen or gives electrons (it is itself oxidised).
Metals which are above hydrogen in the reactivity series will react with dilute hydrochloric or sulfuric acid to produce a salt and hydrogen.
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
For example:
magnesium + hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + hydrogen
Mg (s) + 2HCl (aq) → MgCl₂ (aq) + H₂ (g)
This is a displacement reaction.
There is a rapid fizzing and a colourless gas is produced. This gas pops with a lighted splint, showing the gas is hydrogen.
The reaction mixture becomes warm as heat is produced (exothermic).
The magnesium disappears to leave a colourless solution of magnesium chloride.
If more reactive metals are used instead of magnesium the reaction will be faster so the fizzing will be more vigorous and more heat will be produced.
Tests for gases
| Gas | Test | Result if gas present |
|---|---|---|
| hydrogen (H2) | Use a lit splint | Gas pops |
| oxygen (O2) | Use a glowing splint | Glowing splint relights |
| carbon dioxide (CO2) | Bubble the gas through limewater | Limewater turns cloudy |
| ammonia (NH3) | Use red litmus paper | Turns damp red litmus paper blue |
| chlorine (Cl2) | Use damp litmus paper | Turns damp litmus paper white (bleaches) |