1.04 know and use the relationship between average speed, distance moved and time taken
To calculate average speed use
speed (m/s) = distance travelled (m)/ time taken (s)
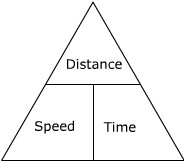
To calculate average speed use
speed (m/s) = distance travelled (m)/ time taken (s)

Weight (N)= Mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg)
gravitational field strength on earth is approx. 10 N/kg and in GCSEs is taken to be 10 N/kg.
units for:
Mass: kilogram (kg)
distance: metre (m)
velocity: metre per second (m/s)
acceleration: metre per second squared (m/s2)
Force: newton (N)
time: second (s)
gravitational field strength: newton/kilogram (N/kg)


The Milky Way galaxy contains billions of stars
The Universe – billions of galaxies
|
An object’s gravitational field strength depends on its MASS. A massive object, like a star, will have a very large g-field. The Moon has less mass than the Earth, so its gravitational field is much weaker – approx 1/6th of the Earth’s. This means that we could jump higher on the Moon, and objects would fall more slowly, as they experience a weaker gravitational force.
A planet with a large radius will have a weaker gravitational field at its surface, because the surface is further away from the centre of the planet. |
According to Newton, there is an attractive gravitational force between any two objects– pulling them together. E.g. the planets and comets experience an attractive force towards the Sun.
Moons and artificial satellites are attracted to their planets, and so are pulled towards them.
This gravitational force keeps them moving in curved paths called orbits. The Moon does not crash into the Earth, and the planets do not crash into the Sun because they are moving.